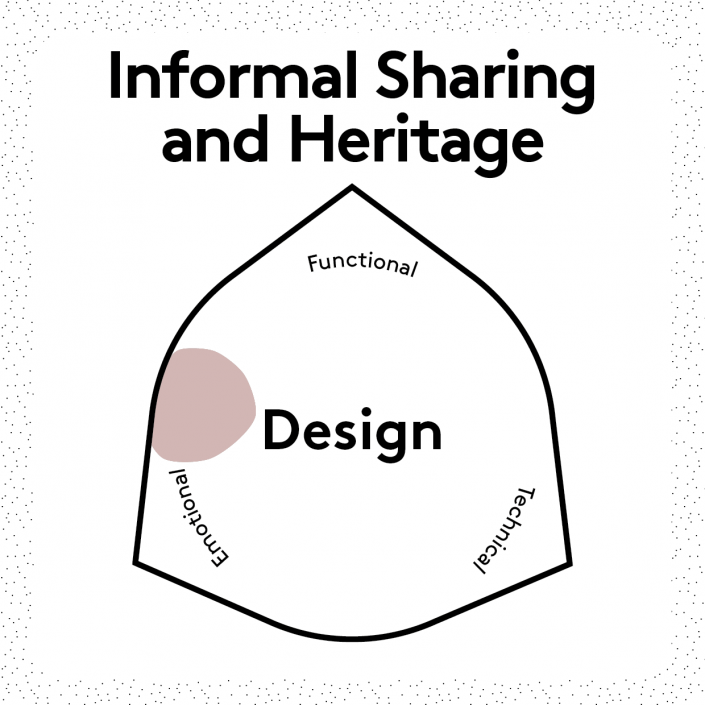
What?
Users that share products in a self-driven and un-systematised manner.
Why?
This approach taps into the current sharing paradigm that focuses on prolonging the lifespan of a product. Sharing and heritage can be:
- An economic advantage.
- A way of passing on/creating emotional value in a product.
Challenges
- Products may not fit new users.
- Unwanted traces of time and use in product may occur such as e.g. smell and stains.
Examples
- People tend to share valuable and little used items, such as baby clothing or fur garments.
- Swapping parties, as with the Copenhagen Fashion Exchange.
- The Freecycle network locally connects people willing to give away free items for others to benefit.
Further Reading
Eden (2017). Blurring the Boundaries: Prosumption, Circularity and Online Sustainable Consumption Through Freecycle. Journal of Consumer Culture, 17(2), 265-285.
Klepp & Laitala (2018). Shared Use and Owning of Clothes: Borrow, Steal or Inherit. In: Contemporary Collaborative Consumption. Springer.
Muñoz & Cohen (2015). Sharing Cities and Sustainable Consumption and Production: Towards an Integrated Framework. Journal of Cleaner Production, 134, 87-97.